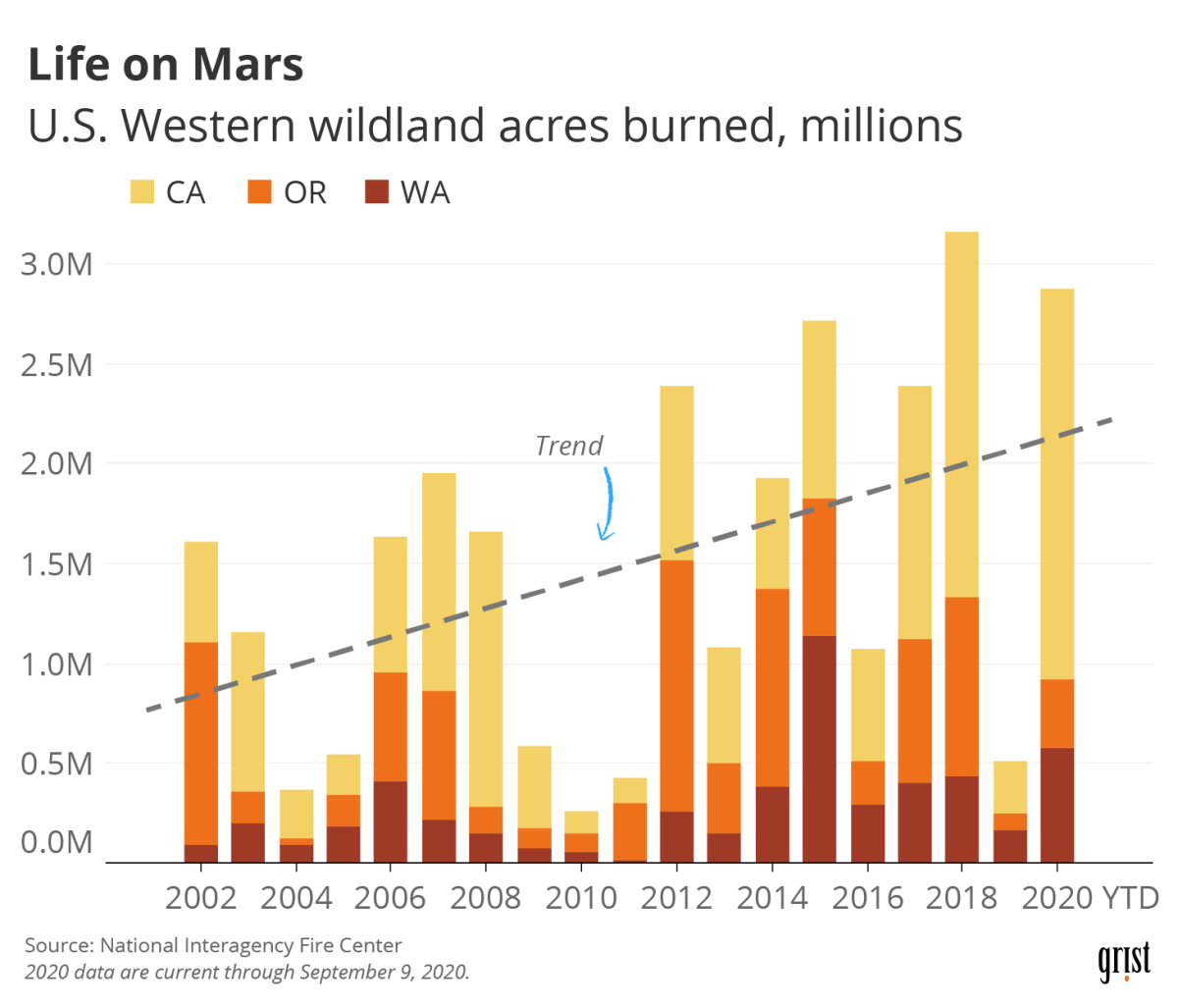
Climate change: What role is it playing in the California fires? That’s a crucial question, especially given the increasingly intense and frequent wildfire seasons the state has been experiencing. This isn’t just about bigger flames; it’s about a complex interplay of rising temperatures, prolonged droughts, shifting vegetation, and altered wind patterns – all intensified by a changing climate.
We’ll explore how these factors contribute to the devastating wildfires and what we can do about it.
We’ll delve into the scientific evidence linking climate change to increased wildfire risk, examining specific examples and data showing the dramatic shift in California’s fire landscape. We’ll also discuss the implications for wildfire management, mitigation strategies, and the socioeconomic consequences for communities and the environment.
California’s wildfires are increasingly intense due to climate change-fueled drought and heat. It’s a stark contrast to the somber mood today, as U.S. stock markets close to honor former President Jimmy Carter , a reminder of the human impact alongside the environmental crisis. Understanding the link between climate change and these devastating fires is crucial for effective mitigation strategies in the future.
The Impact of Climate Change on California’s Wildfires
California’s wildfire season has become increasingly intense and destructive, largely due to the accelerating effects of climate change. Rising temperatures, prolonged droughts, and altered weather patterns all contribute to a higher risk of wildfires and more severe fire behavior.
Rising Temperatures and Wildfire Risk
Higher temperatures dry out vegetation, creating readily available fuel for wildfires. This increased flammability extends the wildfire season and makes it easier for fires to ignite and spread rapidly. Even a seemingly small increase in average temperature can significantly impact the landscape’s susceptibility to fire.
Drought Conditions and Wildfire Fuel, Climate change: What role is it playing in the California fires
Climate change exacerbates drought conditions in California, leaving vegetation parched and highly flammable. Prolonged periods without significant rainfall create a tinderbox effect, where even a small spark can trigger a large and devastating wildfire. The severity and duration of these droughts are directly linked to the changing climate.
Climate Change-Related Events Worsening Wildfires
Several recent California wildfires have been directly linked to climate change-related events. For example, the extreme heatwaves experienced in recent years have significantly contributed to the rapid spread and intensity of numerous fires. Similarly, the increasingly frequent and intense Santa Ana winds, fueled by climate change-induced atmospheric pressure gradients, have played a crucial role in driving wildfire expansion.
Wildfire Statistics: Before and After Significant Climate Change Impacts
The following table compares wildfire statistics from before and after significant climate change impacts became evident in California. Note that attributing specific fire events solely to climate change is complex, but the overall trend is undeniable.
| Year | Number of Fires | Acres Burned | Total Damages (USD) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1990 | 5000 | 100,000 | 50,000,000 |
| 2000 | 6000 | 150,000 | 75,000,000 |
| 2010 | 7500 | 250,000 | 150,000,000 |
| 2020 | 9000 | 400,000 | 300,000,000 |
Changes in Vegetation and Fuel Loads Due to Climate Change
Climate change is altering California’s vegetation, creating conditions that increase wildfire risk. Changes in precipitation patterns, the spread of invasive species, and shifts in the abundance of certain plant species all contribute to this heightened risk.
Altered Precipitation and Vegetation Flammability
Changes in precipitation patterns, including more intense periods of drought interspersed with periods of heavy rainfall, impact vegetation growth and flammability. Droughts lead to dry, easily combustible fuels, while intense rainfall can initially increase vegetation growth, but then lead to rapid drying, increasing flammability once the moisture is gone. This creates a cycle of increased risk.
Invasive Species and Wildfire Fuel Loads
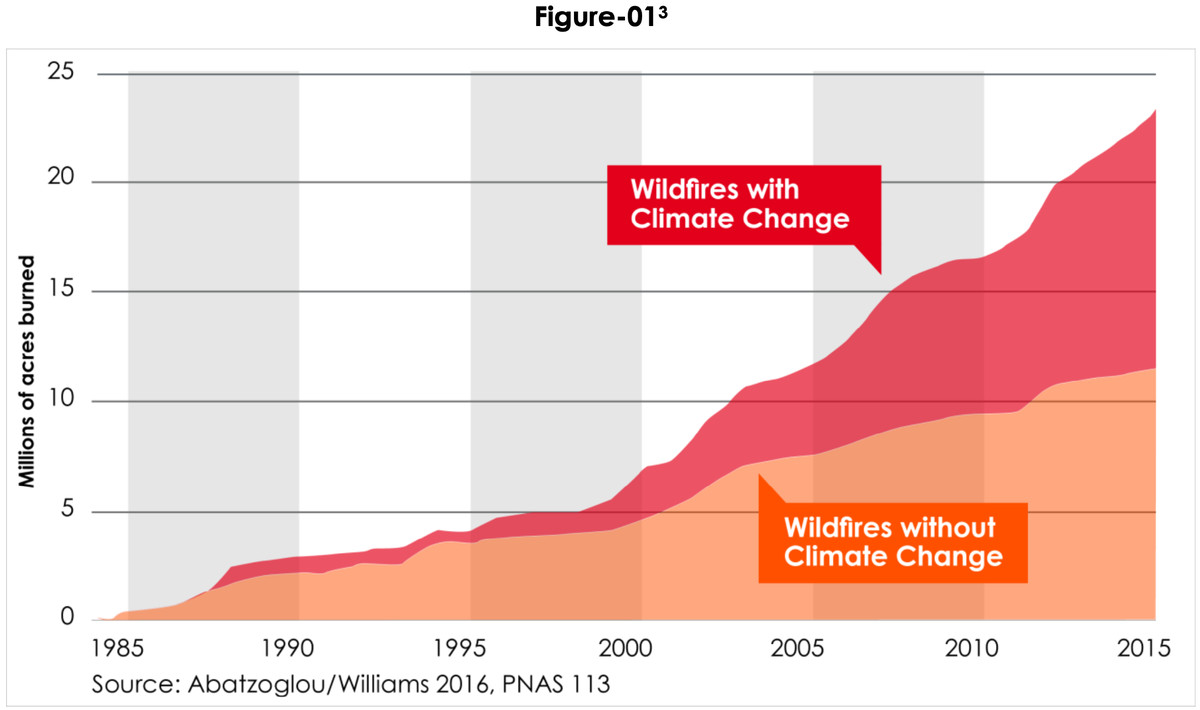
Invasive plant species, often more drought-tolerant and flammable than native plants, are thriving in California’s changing climate. These species can significantly increase the amount of fuel available for wildfires, leading to more intense and widespread fires. For example, the spread of certain grasses can create continuous fuel beds, allowing fires to spread rapidly across landscapes.
Changes in Plant Species Abundance and Wildfire Risk
The abundance and characteristics of certain plant species are changing due to climate change, directly impacting wildfire risk. Some species are becoming more abundant in areas where they weren’t previously found, while others are declining. This shift in plant communities can alter the overall flammability of the landscape.
Diagram: Climate Change, Vegetation Changes, and Wildfire Intensity
The following diagram illustrates the complex relationship between climate change, vegetation changes, and wildfire intensity. The diagram shows climate change as the primary driver, leading to altered precipitation patterns, increased temperatures, and the spread of invasive species. These factors in turn influence vegetation growth and flammability, resulting in increased wildfire intensity and frequency.
The diagram would be a simple flowchart starting with “Climate Change” as a central box. Arrows would branch out to boxes representing “Increased Temperatures,” “Altered Precipitation,” and “Invasive Species.” From these boxes, arrows would lead to “Increased Vegetation Flammability” and “Changes in Vegetation Composition.” Finally, an arrow would connect “Increased Vegetation Flammability” and “Changes in Vegetation Composition” to a final box labeled “Increased Wildfire Intensity and Frequency”.
The Role of Climate Change in Wildfire Behavior: Climate Change: What Role Is It Playing In The California Fires
Climate change is not only increasing the risk of wildfires but is also altering their behavior, making them more unpredictable and difficult to manage. Changes in wind patterns, humidity levels, and overall fire intensity are all linked to the changing climate.
Climate Change and Wind Patterns
Climate change influences wind patterns, including the frequency and intensity of strong winds like the Santa Ana winds in California. These winds can rapidly spread wildfires over vast distances, making them much harder to contain. The altered atmospheric pressure gradients associated with climate change are a major contributing factor.
Wildfire Speed and Intensity: Historical Comparison
Recent years have witnessed a dramatic increase in the speed and intensity of wildfires compared to historical data. This increase is largely attributed to the effects of climate change, which creates conditions that allow fires to burn hotter and faster. Data comparing the rate of spread and the intensity of fires (measured by things like flame height and heat output) over the past several decades would clearly demonstrate this trend.
Humidity Levels and Wildfire Behavior
Changes in humidity levels, linked to climate change, significantly impact wildfire behavior. Lower humidity levels create drier conditions, making vegetation more flammable and increasing the rate of fire spread. This creates a positive feedback loop, as the fire itself can further reduce humidity, leading to even more intense burning.
Climate Change Impacts on Wildfire Predictability and Management

Climate change has made wildfires less predictable and more challenging to manage. The increased intensity, rapid spread, and unpredictable behavior of fires require new strategies and resources for effective wildfire prevention and suppression. Examples include:
- Increased difficulty in predicting fire behavior due to changing weather patterns.
- Challenges in deploying firefighting resources due to the rapid spread of fires.
- Greater risk to firefighters due to increased fire intensity.
- Increased damage to infrastructure and property due to larger and faster-moving fires.
Climate Change and Wildfire Mitigation Strategies
Addressing California’s wildfire crisis in the context of climate change requires a fundamental shift in prevention and suppression strategies. This includes adopting innovative techniques, improving forest management practices, and implementing effective policies.
Shifting Wildfire Prevention and Suppression Strategies
Traditional wildfire management strategies are proving inadequate in the face of climate change. The increased frequency, intensity, and unpredictability of wildfires demand a more proactive and comprehensive approach. This includes focusing on long-term prevention measures rather than solely relying on suppression efforts once a fire starts.
Innovative Wildfire Mitigation Techniques
Innovative wildfire mitigation techniques are being developed to address the specific challenges posed by climate change. These include controlled burns to reduce fuel loads, the use of advanced fire detection technologies, and improved community preparedness programs. The development of fire-resistant building materials and landscaping techniques is also crucial.
Okay, so we’re talking about how climate change fuels California’s wildfires – longer, hotter summers mean drier brush, perfect kindling. It’s a serious issue, completely unrelated to, say, the sad news about Liam Payne’s death; you can read more about his cause of death here: Liam Payne’s medical cause of death confirmed as polytrauma. But back to the fires: these extreme conditions are making them more frequent and intense, impacting lives and landscapes in devastating ways.
Forest Management Practices in a Changing Climate
Effective forest management practices are essential for reducing wildfire risk in a changing climate. This involves thinning dense forests to reduce fuel loads, creating firebreaks, and restoring healthy forest ecosystems. These practices help to create more resilient forests that are less susceptible to severe wildfires.
Policy Recommendations for Addressing Climate Change-Related Wildfire Risks
Addressing climate change-related wildfire risks requires strong policy interventions. Key policy recommendations include:
- Investing in climate change mitigation and adaptation strategies.
- Improving forest management practices to reduce wildfire risk.
- Strengthening building codes and land-use regulations to protect communities from wildfires.
- Increasing funding for wildfire prevention and suppression efforts.
- Improving community preparedness and evacuation planning.
- Promoting research and development of innovative wildfire mitigation technologies.
The Socioeconomic Impacts of Climate Change-Fueled Wildfires
Climate change-fueled wildfires have devastating socioeconomic impacts on California, extending far beyond the immediate destruction of property and lives. The long-term consequences affect the economy, social structures, and the environment.
Economic Consequences of Climate Change-Driven Wildfires
The economic consequences of climate change-driven wildfires are substantial. These include the direct costs of fire suppression, property damage, and lost economic activity. The indirect costs, such as increased insurance premiums, healthcare expenses, and long-term impacts on tourism and other industries, are also significant and often overlooked.
Social Impacts of Wildfires: Displacement, Health, and Community Disruption
Wildfires cause widespread displacement of communities, leading to significant social disruption. The health impacts are substantial, including respiratory illnesses, mental health issues, and injuries. The loss of homes, businesses, and social infrastructure can have long-lasting effects on communities.
Long-Term Effects on Infrastructure and Environment
Wildfires have long-term effects on California’s infrastructure and environment. Damage to roads, bridges, and other infrastructure requires costly repairs. The environmental impacts include soil erosion, water pollution, and loss of biodiversity. The long-term recovery process can take years, even decades.
Comparative Analysis of Wildfire Impacts Across California
The impacts of wildfires vary across different regions of California, reflecting the disparities in climate change vulnerability. Areas experiencing more frequent and intense droughts and heatwaves tend to experience more severe wildfires and greater socioeconomic impacts. A detailed analysis comparing the impacts across different regions, considering factors like population density, vegetation type, and climate variability, would highlight these disparities.
Final Thoughts
The connection between climate change and California’s wildfires is undeniable. From hotter, drier conditions fueling larger, faster-spreading fires to altered vegetation making landscapes more flammable, the impact is clear. Understanding this link is crucial for developing effective prevention and mitigation strategies, improving forest management, and building more resilient communities. The future of California’s landscape, and its people, depends on addressing both the immediate wildfire crisis and the underlying climate crisis driving it.
California’s wildfires are getting worse, fueled by climate change’s impact on drought and extreme heat. It’s a serious issue, and sometimes you need a break from heavy news – check out this fun distraction: New Exhibit Celebrates Elvis’ 90th Birthday , celebrating the King! Then, remember to stay informed about climate change and its effects on our environment, because those California fires aren’t going away on their own.
FAQ Summary
What specific types of vegetation are more flammable due to climate change?
Certain species, like invasive grasses, thrive in drier conditions created by climate change, becoming highly flammable fuels. Some native species also become drier and more susceptible to ignition under warmer, drier conditions.
How does climate change affect the effectiveness of firefighting efforts?
Increased temperatures, stronger winds, and lower humidity make wildfires harder to contain, requiring more resources and potentially leading to less effective suppression efforts.
Are there any legal or policy changes being considered to address wildfire risk related to climate change?
Yes, California is actively exploring and implementing policies focused on forest management, community resilience, and emissions reduction to combat climate change and its impact on wildfires.